The emergence of blockchain technology has introduced the development of digital bonds, a new alternative to traditional bonds that offers a range of benefits. With the ability to issue, trade, and manage bonds on a decentralised and transparent ledger, digital bonds on blockchain are positioned to transform the traditional bond market.
The digital bond market
In the past 18 months, the global bond market has seen the issuance of approximately $1.6 billion in digital bonds.

While this figure is modest compared to the vast traditional bond market, which stood at $133 trillion in 2023, recent pilot programs and experiments led by Eurozone central banks are poised to fuel growth and adoption. Currently, sovereign and supranational entities, and financial and corporate institutions are the primary issuers of digital bonds, with institutional investors dominating the market. However, liquidity remains limited as investors are facing lingering legal hurdles, and regulatory framework is still evolving.
The number of different tokenisation platforms to offer digital bonds creates fragmentation of the market.
As pointed by ESMA, European security markets should move to T+1 settlement in fall of 2027, tokenisation offers potential of instantaneous settlement and transform financial markets.
Benefits of digital bonds on blockchain for issuers
Efficiency and cost reduction
Digital bonds present issuers with significant advantages over traditional bonds in terms of efficiency and cost savings:
- Enhanced settlement times and Reduced counterparty risks: By using Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT), the transaction is either completed in full, instantaneously or not at all (atomicity), preventing scenarios where one party fulfils their obligation while other fails to do so.
- Cost reduction: By using blockchain, digital bonds streamline the issuance process, minimising the need for intermediaries and reducing costs. According to industry research, digital bond issuance could disrupt a $133 trillion market by simplifying transactions and reducing human error with blockchain automation. This is expected to result in notable savings, which could bring more efficient liquidity to the market.
- Transparency: Transactions are recorded on a decentralised ledger, which is natively resistant to tampering due to the decentralised validation process. Issuers and investors can track bond current ownership, payment flows (e.g. coupons), and bond terms in real-time, providing a single source of truth for all parties involved (i.e. issuer, investors, custodians, underwriters, etc..) when doing trade settlements. This enhanced traceability of digital bonds is particularly advantageous for meeting compliance standards for clear history of all transactions, simplifying reconciliation and dispute resolution.
- Reduced overall systemic risk: By minimising the time assets are in transit (in delivery over payment for example), the potential for cascading failures is decreased to none.
These benefits make this innovative instrument attractive for issuers looking to enter the bond market efficiently and cost-effectively.
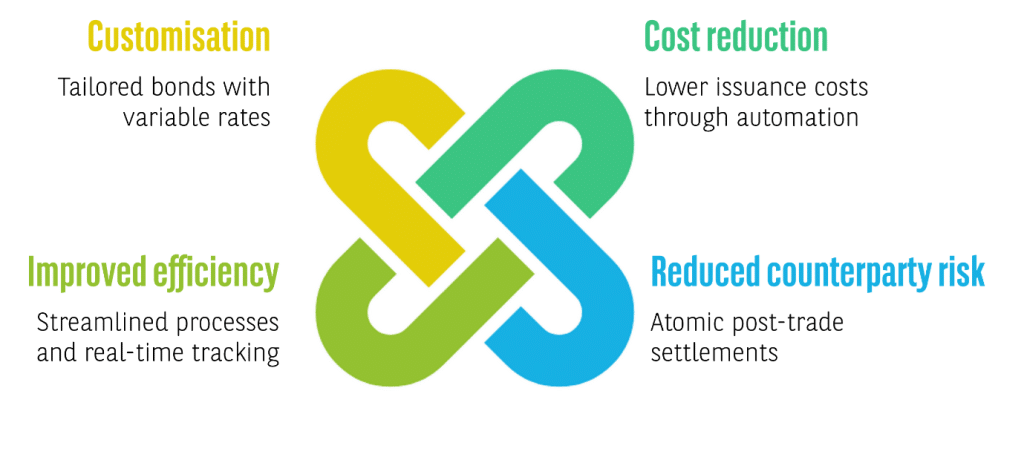
Extended customisation and market reach
- Execution speed: For both origination (i.e. locking funds into a smart contract that will automatically execute upon the deal closing, either transfer to issuer or unlocking to investors) and post-issuance events (ie secondary trading, lifecycle events)
- Risk reduction: The immutability of on-chain records, including corresponding payment legs, reduces the risk of human intervention (i.e. potential market manipulations or unsolicited changes)
- Potential T0 settlements: DLT technology potentially removes open positions between legal commitment and execution (i.e. both occur at the same time – atomicity), reducing the implied market risk and potentially required hedging for the traditional counterparty risk previously involved.
- Environmental Social and Governance (ESG) traceability: Issuers can programme the intended use of the proceeds directly into the bonds terms, for enhanced transparency and compliance of funds allocation.
Unlocking accessibility for investors
While liquidity isn’t there yet, digital bonds could bring several notable advantages for investors:
- Greater accessibility in bond markets: The reduced minimum investment thresholds (e.g. fractional ownership) and 24/7 availability on online marketplaces, makes digital bonds more accessible than traditional bond origination/trading venues. In fact, the digital bond market—though currently small at around $1.6 billion—is expected to grow as more investors seek blockchain-based assets due to their accessibility and efficiency.
- Growing interest from investors: There is a growing interest from investors to explore digital bonds, although only a few actually invested effort required to get familiar with tokenised assets specific and legal framework result in time consuming on boarding process. As the market continues to evolve, investors are also showing appetite to explore different types of digital securities, such as intraday repo (repurchase agreements), on-chain FX settlements and money market funds tokenised.
- Real-time transparency: Blockchain technology provides investors with real-time tracking of bond ownership and transactions.
- Faster settlement times: Compared to traditional 2-3 business days settlement cycle, trading with digital bonds enables instant (i.e minutes, potentially seconds) from buying to ownership (e.g. Delivery over payment).
- Reduced counterparty risks: Using DLTs, digital bonds are openly registered on a shared record keeping where any entitled participant may confirm ownership without relying on counterparty information.
- Process automation and programmability via smart contracts technology: Various bond-related processes, including corporate actions and post-trade events, are built natively to automatically proceed with predefined bond terms.
Comparison table:
| Characteristics | Traditional bonds | Digital bonds |
| Minimum investment threshold | Typically high (e.g., $100,000) | Lower (varies, but often $1,000 or less) |
| Investment channels | Primarily through financial institutions, brokerages, or investment banks | Online marketplaces, blockchain platforms, and digital exchanges |
| Market size | Large, well-established (trillions of dollars) | Currently small ($1.6 billion), but growing rapidly |
| Accessibility | Limited to institutional investors and high-net-worth individuals | Could be accessible to retail investors, including smaller investors |
| Geographic reach | Mainly limited to local markets, with some international access | Global access, with potential for 24/7 trading |
| Investor eligibility | Often restricted to accredited investors or institutional investors | Open to a broader range of investors, including non-accredited investors |
However, liquidity remains limited as the current market is too fragmented and platform on boarding tedious.
What’s missing for the digital market to take off
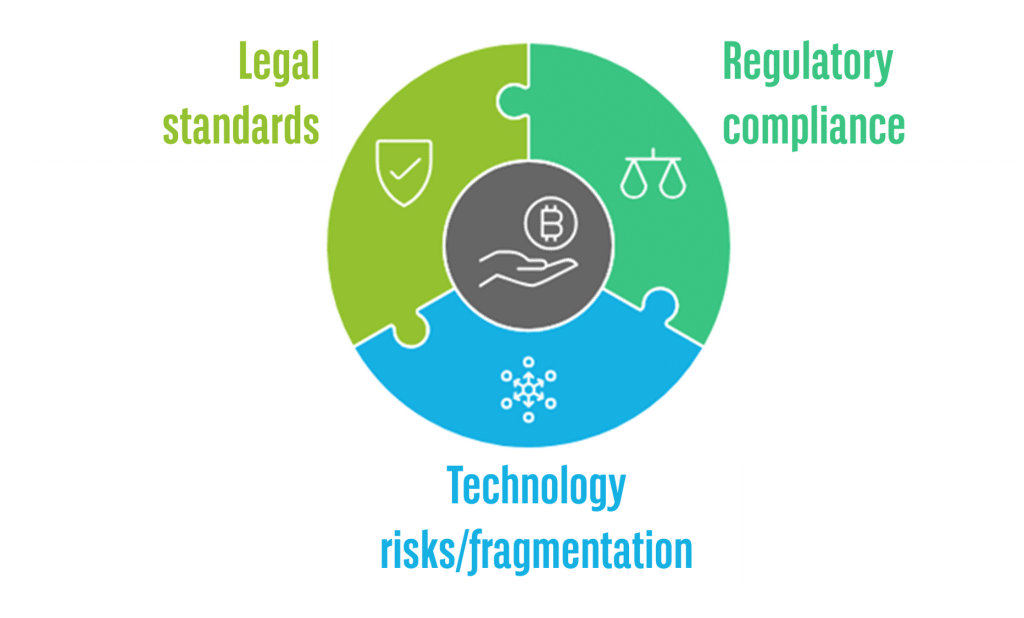
While digital bonds offer significant benefits, challenges remain in their adoption:
- In America, Europe, and Asia, regulators are still defining how to oversee tokenised assets
- Legal standards: harmonised legal frameworks are essential to facilitate cross-border digital bonds transactions in today’s increasingly interconnected global economy.
- Technology interoperability and specifics risks: Being a bleeding-edge and fragmented technology, the battle-testing phase is carefully being analysed for platform stability, ability to interconnect (or being interoperable) and security. Mitigants are usual within digital bond platforms, leveraging on traditional platforms as backup.
BNP Paribas Global Markets’ role in digital bonds: Neobonds tokenisation platform
With its innovative Neobonds platform, BNP Paribas Global Markets is leading the way in this new market.
This blockchain-based solution provides a secure, transparent, and efficient operational framework to support all lifecycle event of bonds issuance issue, manage, and trade digital bonds, but also post trading services.
Example case studies of BNP Paribas in digital bonds:
- European Investment Bank (EIB):
- In January 2023, BNP Paribas co-managed EIB’s inaugural Sterling-denominated digital bond, using both private and public blockchains and raising £50m
- In November 2024, BNP Paribas arranged a €100m digital bond settled with experimental mechanism of wholesale CBDC
- European Central Bank’s Experimentation Program: BNP Paribas participated in this pilot program to assess blockchain’s potential in cost reduction and process efficiency in tokenised bond issuance
With Banque de France’s full DLT cash solution:- BNP Paribas Global Markets issued, distributed and settled on chain with experimental mechanism of digital cash provided by Banque de France, raising €10m (June 2024)
- Republic of Slovenia’s sovereign digital bond (July 2024): BNP Paribas arranged the first Eurozone sovereign digital bond issuance; Axa, Banque de France and EIB invested in secondary market
With Deutsche Bundesbank’s Trigger solution: - In October 2024, BNP Paribas priced, issued and settled a tokenised bond with its Neobonds tokenisation platform as market DLT operator
As part of those issuances, all lifecycle events were processed on chain including secondary trading with BNP Paribas Asset Management, AXA, Banque de France and EIB as investors.
What to expect for the future of digital assets
As the financial landscape continues to evolve, digital assets are emerging as a game-changer.
By offering faster execution, lower costs, and reduced counterparty risks, they’re changing the way we approach financial markets. But it’s not without its challenges. Market participants and regulators are working together to address roadblocks; BNP Paribas playing a key role in Europe to drive the growth of tokenised finance, addressing the evolving needs of our clients by contributing to build bridges across market participants (ie tokenisation platforms, trading venues, exchanges and custodians) to make digital assets a success.
For the digital bond market to grow, it is essential that a network is created to facilitate investor adoption enabling interoperability across all tokenisation platforms, trading venues, exchanges and custodians.
To learn more about how our digital asset expertise can support your financial strategy,
contact us at: DL.GM.Digital.Assets@uk.bnpparibas.com
